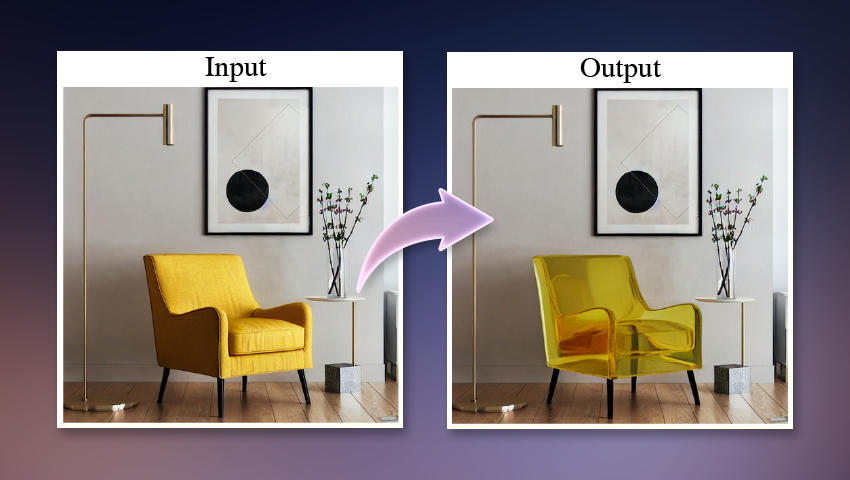
Researchers from the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and Google Research introduced “the alchemist”, A model that provides unprecedented precision in controlling the properties of materials in images. This innovative tool tackles an important challenge encountered by users of generative text models in the image: carrying out detailed and precise material properties.
Alchemist Allows users to modify four key attributes of real images generated by AI:
- Roughness
- Metacicity
- Albedo
- Transparency
Alchemist takes any photo as input and allows users to adjust each property in a continuous scale of -1 to 1, creating a new visual. The magic behind it lies in its dissemination diffusion model, specifically stable diffusion 1.5. This text model in the image is known for its photorealistic results and its editing capacities. Unlike previous diffusion systems which have focused on higher level changes (such as exchange of objects or the modification of the depth of the image), the alchemist takes care of low -level attributes. Its unique interface based on sliders surpasses other methods, allowing precise adjustments to the properties of materials.
Alchemist's design capacities promise significant progress in various fields:
- Video game design: Alchemist could be used to modify video game models, adapt them to different environments or improve their realism.
- Visual effects (VFX): By adjusting the properties of materials, Alchemist could extend the capacities of AI in visual effects, which makes scenes more convincing and immersive.
- Robotic training data: By exposing robots to a wider range of textures, they can better understand and manipulate various elements in real world scenarios. In addition, Alchemist's capacities in the classification of images could help identify neural networks that find it difficult to recognize material changes, thus improving the accuracy of these systems.
In comparative studies, Alchemist has surpassed similar models by accurately modifying only the subject of specified interest. For example, when responsible for making a dolphin fully transparent without modifying the bottom of the ocean, Alchemist was the only model to achieve it with precision. User studies have shown a preference for Alchemist, many finding its outings more photorealistic than those of its counterparts.
To overcome the impracticability of real data collection, the researchers have formed an alchemist on a set of synthetic data. This data set involved attributes of random modification materials of 1,200 materials applied to 100 unique 3D objects in Blender, a popular computer graphics tool.
Despite its progress, Alchemist has certain limits, in particular by precisely deducing the lighting, which can lead to physically incredible results. For example, with maximum transparency parameters, a hand partially inside a cereal box can appear as a clear container without visible fingers.
The research team aims to extend alchemist's abilities. Future work can focus on improving 3D assets for graphics at the scene and to deduce the properties of materials from images, to potentially link visual and mechanical lines.
Watch our YouTube video for a brief demonstration of the magic of the alchemist in action.
